dynamic-import-动态-异步
懒加载在页面上的应用
没有应用懒加载,webpack打包后,会放在一个单独的js文件中会造成这个页面非常大,造成进入首页时,会出现长时间的白屏;
运用懒加载则可以将页面进行划分,需要的时候加载页面,可以有效的分担首页所承担的加载压力,减少首页加载用时。
在Webpack中常用的代码分离方法有三种:
- 入口起点:使用 entry 配置手动地分离代码。
- 防止重复:使用 Entry dependencies 或者 SplitChunksPlugin 去重和分离 chunk。
- 动态导入:通过模块的内联函数调用来分离代码。
Webpack提供两种方法动态代码拆分
- 第一种借助ES6的动态加载模块 - import()
import() 的语法十分简单。该函数只接受一个参数,就是引用模块的地址,并且使用 promise 式的回调获取加载的模块。
通过import()引用的子模块会被单独分离出来,打包成一个单独的文件。
借助import(),我们实现了子模块(子组件)的独立打包(children chunk)。
- 第二种,Webpack 的遗留功能,使用 Webpack 特定的 require.ensure (不推荐使用) ,本文不做探讨 现在,距离实现懒加载(按需加载)还差关键的一步 -- 如何正确使用独立打包的子模块文件(children chunk)实现懒加载。
懒加载分析
import和require 区别
- import 是解构过程并且是编译时执行
- require 是赋值过程并且是运行时才执行,也就是异步加载
分析
懒加载(按需加载)原理分为两步:
- 将需要进行懒加载的子模块打包成独立的文件(children chunk);
- 借助函数来实现延迟执行子模块的加载代码;这里的技术难点就是如何将懒加载的子模块打包成独立的文件。好在ES6提供了import()。
JavaScript函数的特性: 无论使用函数声明还是函数表达式创建函数,函数被创建后并不会立即执行函数内部的代码,只有等到函数被调用之后,才只要将需要进行懒加载的子模块文件(children chunk)的引入语句(本文特指import())放到一个函数内部。然后再需要加载的时候执行该函数。在浏览器运行到这一行代码时,就会自动请求这个资源,实现异步加载。
button.onclick = e => import(/* webpackChunkName: "print" */ './print').then(module => {
const print = module.default;
});
- 第一步:当点击按钮时,拼接请求地址地址,通过 jsonp去加载 print.js 模块所对应的文件
- 第二步:加载回来后在浏览器中执行此JS脚本,将请求过来的模块定义合并到 index.js 中的 modules 中去
- 第三步:合并完后,去加载这个模块
- 第四步:拿到该模块导出的内容
import _ from 'lodash';
function component() {
const element = document.createElement('div');
const button = document.createElement('button');
const br = document.createElement('br');
button.innerHTML = 'Click me and look at the console!';
element.innerHTML = _.join(['Hello', 'webpack'], ' ');
element.appendChild(br);
element.appendChild(button);
button.onclick = e => import(/* webpackChunkName: "print" */ './print').then(module => {
const print = module.default;
print();
});
return element;
}
document.body.appendChild(component());
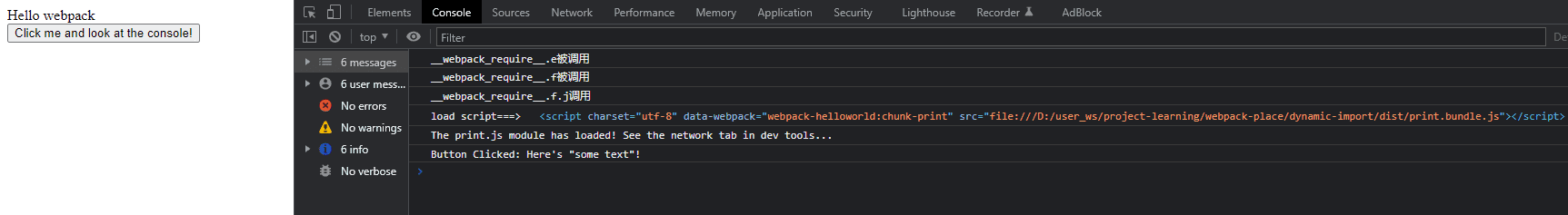
打包后后可以看到点击按钮调用webpack_require.e()
/***/ ((__unused_webpack_module, __webpack_exports__, __webpack_require__) => {
"use strict";
eval("__webpack_require__.r(__webpack_exports__);\n/* harmony import */ var lodash__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__ = __webpack_require__(/*! lodash */ \"./node_modules/lodash/lodash.js\");\n/* harmony import */ var lodash__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0___default = /*#__PURE__*/__webpack_require__.n(lodash__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0__);\n\r\n\r\nfunction component() {\r\n const element = document.createElement('div');\r\n const button = document.createElement('button');\r\n const br = document.createElement('br');\r\n\r\n button.innerHTML = 'Click me and look at the console!';\r\n element.innerHTML = lodash__WEBPACK_IMPORTED_MODULE_0___default().join(['Hello', 'webpack'], ' ');\r\n element.appendChild(br);\r\n element.appendChild(button);\r\n\r\n // Note that because a network request is involved, some indication\r\n // of loading would need to be shown in a production-level site/app.\r\n button.onclick = e => __webpack_require__.e(/*! import() | print */ \"print\").then(__webpack_require__.bind(__webpack_require__, /*! ./print */ \"./src/print.js\")).then(module => {\r\n const print = module.default;\r\n\r\n print();\r\n });\r\n\r\n return element;\r\n}\r\n\r\ndocument.body.appendChild(component());\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack://webpack-helloworld/./src/index.js?");
})
点击后按钮第一步
对应构建源码:构建动态组件源码
build生成index.bundle.js
/* webpack/runtime/ensure chunk */
(() => {
__webpack_require__.f = {};
// This file contains only the entry chunk.
// The chunk loading function for additional chunks
__webpack_require__.e = (chunkId) => {
console.log('__webpack_require__.e被调用')
return Promise.all(Object.keys(__webpack_require__.f).reduce((promises, key) => {
console.log('__webpack_require__.f被调用')
__webpack_require__.f[key](chunkId, promises);
return promises;
}, []));
};
})();
给promises数组赋值,并通过jsonp去加载文件
__webpack_require__.f.j调用__webpack_require__.l
__webpack_require__.f.j = (chunkId, promises) => {
// JSONP chunk loading for javascript
var installedChunkData = __webpack_require__.o(installedChunks, chunkId) ? installedChunks[chunkId] : undefined;
if (installedChunkData !== 0) { // 0 means "already installed".
// a Promise means "currently loading".
if (installedChunkData) {
promises.push(installedChunkData[2]);
} else {
if (true) { // all chunks have JS
// setup Promise in chunk cache
var promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => (installedChunkData = installedChunks[chunkId] = [resolve, reject]));
promises.push(installedChunkData[2] = promise);
// start chunk loading
var url = __webpack_require__.p + __webpack_require__.u(chunkId);
// create error before stack unwound to get useful stacktrace later
var error = new Error();
var loadingEnded = (event) => {
if (__webpack_require__.o(installedChunks, chunkId)) {
installedChunkData = installedChunks[chunkId];
if (installedChunkData !== 0) installedChunks[chunkId] = undefined;
if (installedChunkData) {
var errorType = event && (event.type === 'load' ? 'missing' : event.type);
var realSrc = event && event.target && event.target.src;
error.message = 'Loading chunk ' + chunkId + ' failed.\n(' + errorType + ': ' + realSrc + ')';
error.name = 'ChunkLoadError';
error.type = errorType;
error.request = realSrc;
installedChunkData[1](error);
}
}
};
__webpack_require__.l(url, loadingEnded, "chunk-" + chunkId, chunkId);
} else installedChunks[chunkId] = 0;
}
}
};
最后:执行传入的回调loadingEnded和执行document.head.appendChild(script)
通过 JSONP 去动态引入 chunk 文件,并根据引入的结果状态进行处理,那么我们怎么知道引入之后的状态呢?我们来看异步加载的 chunk 是怎样的
注意:比如当点击按钮时,只需第一次加载时去请求文件,后面加载时应该要去使用缓存。
对应build源码:构建动态组件源码
build之后的源码:index.bundle.js
<!-- 结果 -->
<script charset="utf-8" data-webpack="webpack-helloworld:chunk-print" src="file:///D:/user_ws/project-learning/webpack-place/dynamic-import/dist/print.bundle.js"></script>
可见赋值到__webpack_require__.l对象
(() => {
var inProgress = {};
var dataWebpackPrefix = "webpack-helloworld:";
// loadScript function to load a script via script tag
__webpack_require__.l = (url, done, key, chunkId) => {
if (inProgress[url]) { inProgress[url].push(done); return; }
var script, needAttach;
if (key !== undefined) {
var scripts = document.getElementsByTagName("script");
for (var i = 0; i < scripts.length; i++) {
var s = scripts[i];
if (s.getAttribute("src") == url || s.getAttribute("data-webpack") == dataWebpackPrefix + key) { script = s; break; }
}
}
if (!script) {
needAttach = true;
script = document.createElement('script');
script.charset = 'utf-8';
script.timeout = 120;
if (__webpack_require__.nc) {
script.setAttribute("nonce", __webpack_require__.nc);
}
script.setAttribute("data-webpack", dataWebpackPrefix + key);
script.src = url;
console.log('load script===>', script)
}
inProgress[url] = [done];
var onScriptComplete = (prev, event) => {
// avoid mem leaks in IE.
script.onerror = script.onload = null;
clearTimeout(timeout);
var doneFns = inProgress[url];
delete inProgress[url];
script.parentNode && script.parentNode.removeChild(script);
doneFns && doneFns.forEach((fn) => (fn(event)));
if (prev) return prev(event);
}
var timeout = setTimeout(onScriptComplete.bind(null, undefined, { type: 'timeout', target: script }), 120000);
script.onerror = onScriptComplete.bind(null, script.onerror);
script.onload = onScriptComplete.bind(null, script.onload);
needAttach && document.head.appendChild(script);
};
})();