render阶段2-completeWork
render阶段2:completeWork
render阶段2:completeWork
complete阶段workInProgress节点都是经过diff算法调和过的,也就意味着对于某个节点来说它fiber的形态已经基本确定了,但除此之外还有两点:
- 目前只有fiber形态变了,对于原生DOM组件(HostComponent)和文本节点(HostText)的fiber来说,对应的DOM节点(fiber.stateNode)并未变化。
- 经过Diff生成的新的workInProgress节点持有了flag(即effectTag)
workInProgress节点的completeWork阶段主要做的:
- 真实DOM节点的创建以及挂载
构建过程中,会自下而上将子节点的第一层第一层插入到当前节点。
更新过程中,会计算DOM节点的属性,一旦属性需要更新,会为DOM节点对应的workInProgress节点标记Update的effectTag
- effectList的收集
执行beginWork后会创建子 Fiber 节点,节点上可能存在effectTag。
- DOM属性的处理,次要理解
- 错误处理,次要理解
一旦workInProgress树的所有节点都完成complete,则说明workInProgress树已经构建完成,所有的更新工作已经做完,接下来这棵树会进入commit阶段
如果没有子Fiber节点则返回null, 只有当next为null的时候才会进入completeWork;
当前Fiber节点没有子节点时就进入了completeWork, 可以理解为递归阶段的归阶段。
workLoopSync 循环调用 performUnitOfWork
performUnitOfWork-->completeUnitOfWork-->completeWork
completeWork是一个do while循环, 终止条件有completeWork !== null或者循环内return前的几个终止条件
function performUnitOfWork(unitOfWork) {
workInProgressNums = workInProgressNums + 1
// The current, flushed, state of this fiber is the alternate. Ideally
// nothing should rely on this, but relying on it here means that we don't
// need an additional field on the work in progress.
var current = unitOfWork.alternate;
setCurrentFiber(unitOfWork);
var next;
if ((unitOfWork.mode & ProfileMode) !== NoMode) {
startProfilerTimer(unitOfWork);
//对当前节点进行协调,如果存在子节点,则返回子节点的引用
next = beginWork$1(current, unitOfWork, subtreeRenderLanes);
stopProfilerTimerIfRunningAndRecordDelta(unitOfWork, true);
} else {
next = beginWork$1(current, unitOfWork, subtreeRenderLanes);
}
resetCurrentFiber();
unitOfWork.memoizedProps = unitOfWork.pendingProps;
//如果无子节点,则代表当前的child链表已经遍历完
if (next === null) {
// If this doesn't spawn new work, complete the current work.
//此函数内部会帮我们找到下一个可执行的节点
console.log(`%c 无子节点,则代表当前的child链表已经遍历完,开启子组件链completeUnitOfWork:${unitOfWork.type}`, 'color:black');
completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork);
} else {
workInProgress = next;
}
ReactCurrentOwner$2.current = null;
}
effectList
我们在介绍completeUnitOfWork函数的时候提到,他的其中一个作用是用于进行父节点的effectList的收集:
- 把当前 fiber 节点的 effectList 合并到父节点的effectList中。
- 若当前 fiber 节点存在存在副作用(增,删,改), 则将其加入到父节点的effectList中。
// 将此节点的effectList合并到到父节点的effectList中
if (returnFiber.firstEffect === null) {
returnFiber.firstEffect = completedWork.firstEffect;
}
if (completedWork.lastEffect !== null) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = completedWork.firstEffect;
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = completedWork.lastEffect;
}
// 若当前 fiber 节点存在存在副作用(增,删,改), 则将其加入到父节点的`effectList`中。
const flags = completedWork.flags;
if (flags > PerformedWork) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = completedWork;
} else {
returnFiber.firstEffect = completedWork;
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = completedWork;
}
effectList存在的目的是为了提升commit阶段的工作效率。 在commit阶段,我们需要找出所有存在effectTag的fiber节点并依次执行effectTag对应操作。为了避免在commit阶段再去做遍历操作去寻找effectTag 不为空的fiber节点,React在completeUnitOfWork函数调用的过程中提前把所有存在effectTag的节点收集到effectList中,在commit阶段,只需要遍历effectList,并执行各个节点的effectTag的对应操作就好。
completeUnitOfWork
completeUnitOfWork主要流程
- 调用completeWork。
- 用于进行父节点的effectList的收集:
- 把当前 fiber 节点的 effectList 合并到父节点的effectList中。
- 若当前 fiber 节点存在存在副作用(增,删,改), 则将其加入到父节点的effectList中。
- 沿着此节点所在的兄 -> 弟链表查看其是否拥有兄弟fiber节点(即fiber.sibling !== null),如果存在,则进入其兄弟fiber父 -> 子链表 的遍历(即进入其兄弟节点的beginWork阶段)。如果不存在兄弟fiber,会通过子 -> 父链表回溯到父节点上,直到回溯到根节点,也即完成本次协调
completeUnitOfWork 从源码中可以看到是一个do while循环, 终止条件有completeWork !== null或者循环内return前的几个终止条件, 我们可以看到有一个是siblingFiber不为null的情况. 即当前的节点存在兄弟节点时并且已经没有子节点, 当前节点会结束completeWork, 跳出调用栈, 执行下一次循环, 进入兄弟节点的beginWork.当兄弟节点为null的时候, 那么completeWork会被赋值为returnFiber, 这个时候注意并没有用return跳出调用栈, 因为父级节点的beginWork已经被执行, 因此会进入父级节点的completeWork, 由此向上, 当completeWork为null时意味着归到根节点
function completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork) {
var completedWork = unitOfWork;
do {
var current = completedWork.alternate;
var returnFiber = completedWork.return; // Check if the work completed or if something threw.
if ((completedWork.flags & Incomplete) === NoFlags) {
setCurrentFiber(completedWork);
var next = void 0;
if ((completedWork.mode & ProfileMode) === NoMode) {
console.log(`%c ==开始completeWork-1`, 'color:black')
next = completeWork(current, completedWork, subtreeRenderLanes);
} else {
console.log(`%c ==开始completeWork-2`, 'color:black')
startProfilerTimer(completedWork);
next = completeWork(current, completedWork, subtreeRenderLanes); // Update render duration assuming we didn't error.
stopProfilerTimerIfRunningAndRecordDelta(completedWork, false);
}
resetCurrentFiber();
if (next !== null) {
// Completing this fiber spawned new work. Work on that next.
workInProgress = next;
return;
}
}else{
// ...
}
// 查看当前节点是否存在兄弟节点
var siblingFiber = completedWork.sibling;
if (siblingFiber !== null) {
// If there is more work to do in this returnFiber, do that next.
// 若存在,便把siblingFiber节点作为下一个工作单元,
// 继续执行performUnitOfWork,执行当前节点并尝试遍历当前节点所在的child链表
workInProgress = siblingFiber;
return;
}
// 如果不存在兄弟节点,则回溯到父节点,尝试查找父节点的兄弟节点
completedWork = returnFiber; // Update the next thing we're working on in case something throws.
workInProgress = completedWork;
} while (completedWork !== null); // We've reached the root.
}
正式进入completeWork
completeWork的作用包括:
- 为新增的 fiber 节点生成对应的DOM节点。
- 更新DOM节点的属性。
- 进行事件绑定。
- 收集effectTag。
类似 beginWork,completeWork 也是针对不同 fiber.tag 调用不同的处理逻辑。
重点关注页面渲染所必须的 HostComponent(即原生 DOM 组件对应的 Fiber 节点),
同时针对 HostComponent ,判断update时我们还需要考虑 workInProgress.stateNode != null ?(即该 Fiber 节点是否存在对应的 DOM 节点)。
case HostComponent为例子:
还记得我们讲到:mount 时只会在 rootFiber 存在 Placement effectTag。那么commit 阶段是如何通过一次插入 DOM 操作(对应一个Placement effectTag)将整棵 DOM 树插入页面的呢?
原因就在于 completeWork 中的appendAllChildren 方法。
由于 completeWork 属于“归”阶段调用的函数,每次调用 appendAllChildren 时都会将已生成的子孙 DOM 节点插入当前生成的 DOM 节点下。那么当“归”到 rootFiber 时,我们已经有一个构建好的离屏 DOM 树。
hostComponent为例子:
根据current状态进入不同逻辑,我们分析首屏渲染时的逻辑,主要有以下几步:
- createInstance 为当前fiber创建dom实例
createInstance =>
createElement =>
document.createElement
appendAllChildren 遍历所有同级子代节点,执行父节点的appenChild方法,即此方法会将所有子dom节点与当前创建的dom实例连接
赋值stateNode属性
finalizeInitialChildren 处理props
至此,首屏渲染时render阶段的大体流程就梳理完了
function completeWork(current, workInProgress, renderLanes) {
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
case LazyComponent:
case SimpleMemoComponent:
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case Fragment:
case Mode:
case Profiler:
case ContextConsumer:
case MemoComponent:
return null;
case ClassComponent: {
// ...省略
return null;
}
case HostRoot: {
// ...省略
updateHostContainer(workInProgress);
return null;
}
case HostComponent:
{
popHostContext(workInProgress);
var rootContainerInstance = getRootHostContainer();
var type = workInProgress.type;
if (current !== null && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {
console.log(`%c=completeWork->更新流程HostComponent调用updateHostComponent`, 'color:chartreuse')
updateHostComponent(current, workInProgress, type, newProps, rootContainerInstance);
if (current.ref !== workInProgress.ref) {
markRef(workInProgress);
}
} else {
if (!newProps) {
if (workInProgress.stateNode === null) {
throw new Error('We must have new props for new mounts. This error is likely ' + 'caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.');
} // This can happen when we abort work.
bubbleProperties(workInProgress);
return null;
}
var currentHostContext = getHostContext(); // TODO: Move createInstance to beginWork and keep it on a context
// "stack" as the parent. Then append children as we go in beginWork
// or completeWork depending on whether we want to add them top->down or
// bottom->up. Top->down is faster in IE11.
var _wasHydrated = popHydrationState(workInProgress);
if (_wasHydrated) {
// TODO: Move this and createInstance step into the beginPhase
// to consolidate.
if (prepareToHydrateHostInstance(workInProgress, rootContainerInstance, currentHostContext)) {
// If changes to the hydrated node need to be applied at the
// commit-phase we mark this as such.
markUpdate(workInProgress);
}
} else {
// 为当前fiber创建dom实例
console.log('%c=beginWork->HostComponent初始化流程调用createInstance为当前fiber创建dom实例==>start', 'color:chartreuse')
var instance = createInstance(type, newProps, rootContainerInstance, currentHostContext, workInProgress);
// 将子孙dom节点追加到当前创建的dom节点上
console.log('%c=beginWork->HostComponent初始化流程-将子孙dom节点追加到当前创建的dom节点上', 'color:green', { instance })
appendAllChildren(instance, workInProgress, false, false);
// 将当前创建的挂载到stateNode属性上
workInProgress.stateNode = instance; // Certain renderers require commit-time effects for initial mount.
console.log('%c=beginWork->HostComponent初始化流程将当前创建的挂载到workInProgress.stateNode:', 'color:green', { workInProgress_stateNode: workInProgress.stateNode });
// (eg DOM renderer supports auto-focus for certain elements).
// Make sure such renderers get scheduled for later work.
// 处理props(绑定回调,设置dom属性...)
if (finalizeInitialChildren(instance, type, newProps, rootContainerInstance)) {
markUpdate(workInProgress);
}
}
// ref属性相关逻辑
if (workInProgress.ref !== null) {
// If there is a ref on a host node we need to schedule a callback
markRef(workInProgress);
}
}
bubbleProperties(workInProgress);
return null;
}
}
调用createElement为当前fiber创建dom节点
function createElement(type, props, rootContainerElement, parentNamespace) {
var isCustomComponentTag; // We create tags in the namespace of their parent container, except HTML
// tags get no namespace.
var ownerDocument = getOwnerDocumentFromRootContainer(rootContainerElement);
var domElement;
var namespaceURI = parentNamespace;
if (namespaceURI === HTML_NAMESPACE) {
namespaceURI = getIntrinsicNamespace(type);
}
if (namespaceURI === HTML_NAMESPACE) {
{
isCustomComponentTag = isCustomComponent(type, props); // Should this check be gated by parent namespace? Not sure we want to
// allow <SVG> or <mATH>.
if (!isCustomComponentTag && type !== type.toLowerCase()) {
error('<%s /> is using incorrect casing. ' + 'Use PascalCase for React components, ' + 'or lowercase for HTML elements.', type);
}
}
if (type === 'script') {
// Create the script via .innerHTML so its "parser-inserted" flag is
// set to true and it does not execute
var div = ownerDocument.createElement('div');
div.innerHTML = '<script><' + '/script>'; // eslint-disable-line
// This is guaranteed to yield a script element.
var firstChild = div.firstChild;
domElement = div.removeChild(firstChild);
} else if (typeof props.is === 'string') {
// $FlowIssue `createElement` should be updated for Web Components
domElement = ownerDocument.createElement(type, {
is: props.is
});
} else {
// Separate else branch instead of using `props.is || undefined` above because of a Firefox bug.
// See discussion in https://github.com/facebook/react/pull/6896
// and discussion in https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=1276240
domElement = ownerDocument.createElement(type); // Normally attributes are assigned in `setInitialDOMProperties`, however the `multiple` and `size`
// attributes on `select`s needs to be added before `option`s are inserted.
// This prevents:
// - a bug where the `select` does not scroll to the correct option because singular
// `select` elements automatically pick the first item #13222
// - a bug where the `select` set the first item as selected despite the `size` attribute #14239
// See https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/13222
// and https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/14239
if (type === 'select') {
var node = domElement;
if (props.multiple) {
node.multiple = true;
} else if (props.size) {
// Setting a size greater than 1 causes a select to behave like `multiple=true`, where
// it is possible that no option is selected.
//
// This is only necessary when a select in "single selection mode".
node.size = props.size;
}
}
}
} else {
domElement = ownerDocument.createElementNS(namespaceURI, type);
}
{
if (namespaceURI === HTML_NAMESPACE) {
if (!isCustomComponentTag && Object.prototype.toString.call(domElement) === '[object HTMLUnknownElement]' && !hasOwnProperty.call(warnedUnknownTags, type)) {
warnedUnknownTags[type] = true;
error('The tag <%s> is unrecognized in this browser. ' + 'If you meant to render a React component, start its name with ' + 'an uppercase letter.', type);
}
}
}
console.log(`%c=createElement`, 'color:green', { type, props, domElement })
return domElement;
}
appendAllChildren负责将子孙DOM节点插入刚生成的DOM节点中
beginWork时介绍过,在mount时,为了避免每个fiber节点都需要进行插入操作,在mount时,只有根节点会收集effectTag, 其余节点不会进行effectTag的收集。由于每次执行appendAllChildren后,我们都能得到一棵以当前workInProgress为 根节点的DOM树。因此在commit阶段我们只需要对mount的根节点进行一次插入操作就可以了。
appendAllChildren = function(
parent: Instance,
workInProgress: Fiber,
needsVisibilityToggle: boolean,
isHidden: boolean,
) {
// 获取workInProgress的子fiber节点
let node = workInProgress.child;
// 当存在子节点时,去往下遍历
while (node !== null) {
if (node.tag === HostComponent || node.tag === HostText) {
// 当node节点为HostComponent后HostText时,直接插入到子DOM节点列表的尾部
appendInitialChild(parent, node.stateNode);
} else if (enableFundamentalAPI && node.tag === FundamentalComponent) {
appendInitialChild(parent, node.stateNode.instance);
} else if (node.tag === HostPortal) {
// 当node节点为HostPortal类型的节点,什么都不做
} else if (node.child !== null) {
// 上面分支都没有命中,说明node节点不存在对应DOM,向下查找拥有stateNode属性的子节点
node.child.return = node;
node = node.child;
continue;
}
if (node === workInProgress) {
// 回溯到workInProgress时,以添加完所有子节点
return;
}
// 当node节点不存在兄弟节点时,向上回溯
while (node.sibling === null) {
// 回溯到workInProgress时,以添加完所有子节点
if (node.return === null || node.return === workInProgress) {
return;
}
node = node.return;
}
// 此时workInProgress的第一个子DOM节点已经插入到进入workInProgress对应的DOM节点了,开始进入node节点的兄弟节点的插入操作
node.sibling.return = node.return;
node = node.sibling;
}
};
解析:在"归"阶段会调用completeWork处理 Fiber 节点
completeWork 将根据 workInProgress 节点的 tag 属性的不同,进入不同的 DOM 节点的创建、处理逻辑。
completeWork 内部有 3 个关键动作:
- 创建 DOM 节点(CreateInstance)
- 将 DOM 节点插入到 DOM 树中(AppendAllChildren)
- 为 DOM 节点设置属性(FinalizeInitialChildren)
当某个 Fiber 节点执行完completeWork,如果其存在兄弟 Fiber 节点(即fiber.sibling !== null),会进入其兄弟 Fiber 的"递"阶段。
如果不存在兄弟 Fiber,会进入父级 Fiber 的"归"阶段。
"递"和"归"阶段会交错执行直到"归"到 rootFiber。至此,协调阶段的工作就结束了。
更新阶段
会根据新的状态形成的jsx(ClassComponent的render或者FuncComponent的返回值)和current Fiber对比形(diff算法)构建workInProgress的Fiber树
然后将fiberRoot的current指向workInProgress树,此时workInProgress就变成了current Fiber。
在update的时候,render阶段会根据最新的jsx和老的Fiber进行对比,生成新的Fiber。 这些Fiber会带有各种副作用,比如‘Deletion’、‘Update’、‘Placement’等,这一个对比的过程就是diff算法 ,在commit阶段会操作真实节点,执行相应的副作用。
diff ⽐较的是什么? ⽐较的是 current fiber 和 vdom,⽐较之后⽣成 workInProgress Fiber
render阶段会根据最新的jsx生成的虚拟dom和current Fiber树进行对比,比较之后生成workInProgress Fiber(workInProgress Fiber树的alternate指向Current Fiber树的对应节点,这些Fiber会带有各种副作用,比如‘Deletion’、‘Update’、'Placement’等)这一对比过程就是diff算法
当workInProgress Fiber树构建完成,workInProgress 则成为了current Fiber渲染到页面上
render阶段之update时: fiber 双缓存 和 diff;beginWork与completeWork的不同
在update diff 比较时: 就是在构建 workInProgress fiber tree 的过程中,会根据新的状态形成的jsx(ClassComponent的render或者FuncComponent的返回值)和current Fiber对比形(diff算法)构建workInProgress的Fiber树。
判断 current fiber tree 中的 fiber node 是否可以被 workInProgress fiber tree 复用。
能被复用,意味在本次更新中,需要做:
组件的 update 以及 dom 节点的 move、update 等操作;
不可复用,则意味着需要做:
组件的 mount、unmount 以及 dom 节点的 insert、delete 等操作。
当更新完成以后,fiberRootNode 的 current 指针会指向 workInProgress fiber tree,作为下一次更新的 current fiber tree
当 update 时,Fiber 节点已经存在对应 DOM 节点,所以不需要生成 DOM 节点。需要做的主要是处理 props,比如:
- onClick、onChange 等回调函数的注册;
- 处理style prop;
- 处理DANGEROUSLY_SET_INNER_HTML prop;
- 处理children prop。
我们去掉一些当前不需要关注的功能(比如 ref)。可以看到最主要的逻辑是调用 updateHostComponent 方法。你可以从这里看到updateHostComponent 方法定义。
在 updateHostComponent 内部,被处理完的 props 会被赋值给 workInProgress.updateQueue,并最终会在 commit 阶段被渲染在页面上。
workInProgress.updateQueue = (updatePayload: any);
其中updatePayload为数组形式,他的奇数索引的值为变化的 prop key,偶数索引的值为变化的 prop value。
render阶段之update时两个函数对比
function beginWork(current, workInProgress, renderLanes) {
// mount current !== null 为null,不走以下逻辑
if (current !== null) {
console.log('%c=beginWork()===start1-更新', 'color:magenta', { getFiberName: getFiberName(workInProgress), current, renderLanes, workInProgress })
// 通过一系列判断逻辑判断当前节点是否可复用,用didReceiveUpdate来标记,
}{
console.log('%c=beginWork()===start1-初始化', 'color:magenta', { getFiberName: getFiberName(workInProgress), current, renderLanes, workInProgress })
workInProgress.lanes = NoLanes;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
// ...省略
case LazyComponent:
// ...省略
case FunctionComponent:
// ...省略
case ClassComponent:
// ...省略
case HostRoot:
// ...省略
case HostComponent:
console.log(`%c=beginWork()=end 7 updateHostComponent$1,即原生 DOM 组件对应的 Fiber节点:`, 'color:magenta', { type: workInProgress.type })
return updateHostComponent$1(current, workInProgress, renderLanes);
case HostText:
}
}
}
function completeWork(current, workInProgress, renderLanes) {
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
case LazyComponent:
case SimpleMemoComponent:
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case Fragment:
case Mode:
case Profiler:
case ContextConsumer:
case MemoComponent:
return null;
case ClassComponent: {
// ...省略
return null;
}
case HostRoot: {
// ...省略
updateHostContainer(workInProgress);
return null;
}
case HostComponent:
{
popHostContext(workInProgress);
var rootContainerInstance = getRootHostContainer();
var type = workInProgress.type;
if (current !== null && workInProgress.stateNode != null) {
console.log(`%c=completeWork->更新流程HostComponent调用updateHostComponent`, 'color:chartreuse')
updateHostComponent(current, workInProgress, type, newProps, rootContainerInstance);
if (current.ref !== workInProgress.ref) {
markRef(workInProgress);
}
} else {
if (!newProps) {
if (workInProgress.stateNode === null) {
throw new Error('We must have new props for new mounts. This error is likely ' + 'caused by a bug in React. Please file an issue.');
} // This can happen when we abort work.
bubbleProperties(workInProgress);
return null;
}
var currentHostContext = getHostContext(); // TODO: Move createInstance to beginWork and keep it on a context
// "stack" as the parent. Then append children as we go in beginWork
// or completeWork depending on whether we want to add them top->down or
// bottom->up. Top->down is faster in IE11.
var _wasHydrated = popHydrationState(workInProgress);
if (_wasHydrated) {
// TODO: Move this and createInstance step into the beginPhase
// to consolidate.
if (prepareToHydrateHostInstance(workInProgress, rootContainerInstance, currentHostContext)) {
// If changes to the hydrated node need to be applied at the
// commit-phase we mark this as such.
markUpdate(workInProgress);
}
} else {
// 为当前fiber创建dom实例
console.log('%c=beginWork->HostComponent初始化流程调用createInstance为当前fiber创建dom实例==>start', 'color:chartreuse')
var instance = createInstance(type, newProps, rootContainerInstance, currentHostContext, workInProgress);
// 将子孙dom节点追加到当前创建的dom节点上
console.log('%c=beginWork->HostComponent初始化流程-将子孙dom节点追加到当前创建的dom节点上', 'color:green', { instance })
appendAllChildren(instance, workInProgress, false, false);
// 将当前创建的挂载到stateNode属性上
workInProgress.stateNode = instance; // Certain renderers require commit-time effects for initial mount.
console.log('%c=beginWork->HostComponent初始化流程将当前创建的挂载到workInProgress.stateNode:', 'color:green', { workInProgress_stateNode: workInProgress.stateNode });
// (eg DOM renderer supports auto-focus for certain elements).
// Make sure such renderers get scheduled for later work.
// 处理props(绑定回调,设置dom属性...)
if (finalizeInitialChildren(instance, type, newProps, rootContainerInstance)) {
markUpdate(workInProgress);
}
}
// ref属性相关逻辑
if (workInProgress.ref !== null) {
// If there is a ref on a host node we need to schedule a callback
markRef(workInProgress);
}
}
bubbleProperties(workInProgress);
return null;
}
}
update流程我们只需抓住与mount的不同:current不为null,由于二者的不同主要体现在render阶段,因为我们分别分析beginWork与completeWork的不同。
update流程之beginWork current不为null的逻辑:
通过一系列判断逻辑判断当前节点是否可复用,用didReceiveUpdate来标记, 若可复用则走attemptEarlyBailoutIfNoScheduledUpdate。调用栈如下:
顾名思义,会直接克隆一个fiber节点并返回。
attemptEarlyBailoutIfNoScheduledUpdate =>bailoutOnAlreadyFinishedWork=>cloneChildFibers
update流程之beginWork第二阶段
beginWork第二阶段的逻辑是mount与update共用的,当节点无法复用时会调用 reconcileChildren 生成子节点, 其内部会根据current是否存在进入 mountChildFibers(current为null)或 reconcileChildFibers(current不为null),
我们已经知道这两者的逻辑基本是相同的,只是 reconcileChildFibers 会为当前fiber打上 flags,它代表当前dom需要执行的操作(插入,更新,删除等),
function placeSingleChild(newFiber: Fiber): Fiber {
// shouldTrackSideEffects代表需要追踪副作用,update时会将其标记为true
// 当前fiber不存在dom实例时,才可标记Placement
if (shouldTrackSideEffects && newFiber.alternate === null) {
newFiber.flags |= Placement;
}
return newFiber;
}
另外,由于mount时current不存在,因此reconcileChildFibers不会有对比更新的逻辑,直接创建节点,而update时则会将current与当前的ReactElement 做对比生成WIP,也就是diff算法,具体实现细节这里不展开
update流程之completeWork-->updateHostComponent
updateHostComponent 用于更新DOM节点的属性并在当前节点存在更新属性,收集Update effectTag。
根据需代码: 要变化的prop会被存储到updatePayload 中,updatePayload 为一个偶数索引的值为变化的prop key,奇数索引的值为变化的prop value的数组。 并最终挂载到挂载到workInProgress.updateQueue上,供后续commit阶段使用。
我们已经知道,mount时completeWork会直接创建dom实例,而update会调用updateHostComponent,我们来分析其实现逻辑:
在新旧props不同时调用prepareUpdate,他会对比新旧props并生成updatePayload,其调用栈如下:
prepareUpdate-->diffProperties
diffProperties内部主逻辑是对props进行两轮循环,分别处理属性删除与属性新增的情况,最终返回updatePayload,这是一个数组, 第i项和第i+1项分别是更新后的的key和value。他会在mutation阶段被用于更新节点属性。 updateHostComponent的最后调用进行markUpdate,赋值更新的flags(Update)。
updateHostComponent = function (current, workInProgress, type, newProps, rootContainerInstance) {
// If we have an alternate, that means this is an update and we need to
// schedule a side-effect to do the updates.
var oldProps = current.memoizedProps;
console.log(`%c=updateHostComponent更新流程`, 'color:chartreuse')
if (oldProps === newProps) {
// In mutation mode, this is sufficient for a bailout because
// we won't touch this node even if children changed.
return;
} // If we get updated because one of our children updated, we don't
// have newProps so we'll have to reuse them.
// TODO: Split the update API as separate for the props vs. children.
// Even better would be if children weren't special cased at all tho.
var instance = workInProgress.stateNode;
var currentHostContext = getHostContext(); // TODO: Experiencing an error where oldProps is null. Suggests a host
// component is hitting the resume path. Figure out why. Possibly
// related to `hidden`.
// 对比props生成updatePayload
var updatePayload = prepareUpdate(instance, type, oldProps, newProps, rootContainerInstance, currentHostContext); // TODO: Type this specific to this type of component.
workInProgress.updateQueue = updatePayload; // If the update payload indicates that there is a change or if there
// is a new ref we mark this as an update. All the work is done in commitWork.
if (updatePayload) {
markUpdate(workInProgress);
}
};
function diffProperties(
domElement: Element,
tag: string,
lastRawProps: Object,
nextRawProps: Object,
rootContainerElement: Element | Document,
): null | Array<mixed> {
let updatePayload: null | Array<any> = null;
let lastProps: Object;
let nextProps: Object;
//处理新旧props 针对表单标签做特殊处理
switch (tag) {
case 'input':
lastProps = ReactDOMInputGetHostProps(domElement, lastRawProps);
nextProps = ReactDOMInputGetHostProps(domElement, nextRawProps);
updatePayload = [];
break;
case 'select':
lastProps = ReactDOMSelectGetHostProps(domElement, lastRawProps);
nextProps = ReactDOMSelectGetHostProps(domElement, nextRawProps);
updatePayload = [];
break;
case 'textarea':
lastProps = ReactDOMTextareaGetHostProps(domElement, lastRawProps);
nextProps = ReactDOMTextareaGetHostProps(domElement, nextRawProps);
updatePayload = [];
break;
default:
lastProps = lastRawProps;
nextProps = nextRawProps;
if (
typeof lastProps.onClick !== 'function' &&
typeof nextProps.onClick === 'function'
) {
// TODO: This cast may not be sound for SVG, MathML or custom elements.
trapClickOnNonInteractiveElement(((domElement: any): HTMLElement));
}
break;
}
assertValidProps(tag, nextProps);
let propKey;
let styleName;
let styleUpdates = null;
for (propKey in lastProps) {
if (
nextProps.hasOwnProperty(propKey) ||
!lastProps.hasOwnProperty(propKey) ||
lastProps[propKey] == null
) {
continue;
}
// 新无旧有时进入一下逻辑,即属性被删除
if (propKey === STYLE) {
const lastStyle = lastProps[propKey];
// 将对应style属性置空
for (styleName in lastStyle) {
if (lastStyle.hasOwnProperty(styleName)) {
if (!styleUpdates) {
styleUpdates = {};
}
styleUpdates[styleName] = '';
}
}
} else {
// 将对应key及value(null)推入更新队列,
(updatePayload = updatePayload || []).push(propKey, null);
}
}
for (propKey in nextProps) {
const nextProp = nextProps[propKey];
const lastProp = lastProps != null ? lastProps[propKey] : undefined;
if (
!nextProps.hasOwnProperty(propKey) ||
nextProp === lastProp ||
(nextProp == null && lastProp == null)
) {
continue;
}
// 新有旧无或新旧都有切不相等时进入以下逻辑
// style属性特殊处理 总结如下
// 新有旧无 推入style队列
// 新旧都有 用新的
// 新无旧有 将对应属性置空
if (propKey === STYLE) {
if (lastProp) {
for (styleName in lastProp) {
if (
lastProp.hasOwnProperty(styleName) &&
(!nextProp || !nextProp.hasOwnProperty(styleName))
) {
if (!styleUpdates) {
styleUpdates = {};
}
styleUpdates[styleName] = '';
}
}
for (styleName in nextProp) {
if (
nextProp.hasOwnProperty(styleName) &&
lastProp[styleName] !== nextProp[styleName]
) {
if (!styleUpdates) {
styleUpdates = {};
}
styleUpdates[styleName] = nextProp[styleName];
}
}
} else {
if (!styleUpdates) {
if (!updatePayload) {
updatePayload = [];
}
updatePayload.push(propKey, styleUpdates);
}
styleUpdates = nextProp;
}
} else {
// 将对应key及value推入更新队列
(updatePayload = updatePayload || []).push(propKey, nextProp);
}
}
if (styleUpdates) {
(updatePayload = updatePayload || []).push(STYLE, styleUpdates);
}
return updatePayload;
}
update流程之completeWork:这个tag标识有什么用呢
render阶段组件更新会根据checkHasForceUpdateAfterProcessing,和checkShouldComponentUpdate来判断,
如果Update的tag是ForceUpdate,则 checkHasForceUpdateAfterProcessing 为true,当组件是PureComponent时; checkShouldComponentUpdate 会浅比较state和props,所以当使用this.forceUpdate一定会更新.
function resumeMountClassInstance(workInProgress, ctor, newProps, renderLanes) {
var instance = workInProgress.stateNode;
var oldProps = workInProgress.memoizedProps;
instance.props = oldProps;
var oldContext = instance.context;
var contextType = ctor.contextType;
var nextContext = emptyContextObject;
...
var shouldUpdate = checkHasForceUpdateAfterProcessing() || checkShouldComponentUpdate(workInProgress, ctor, oldProps, newProps, oldState, newState, nextContext);
if (shouldUpdate) {
// In order to support react-lifecycles-compat polyfilled components,
// Unsafe lifecycles should not be invoked for components using the new APIs.
if (!hasNewLifecycles && (typeof instance.UNSAFE_componentWillMount === 'function' || typeof instance.componentWillMount === 'function')) {
if (typeof instance.componentWillMount === 'function') {
instance.componentWillMount();
}
if (typeof instance.UNSAFE_componentWillMount === 'function') {
instance.UNSAFE_componentWillMount();
}
}
if (typeof instance.componentDidMount === 'function') {
workInProgress.flags |= Update;
}
} else {
// If an update was already in progress, we should schedule an Update
// effect even though we're bailing out, so that cWU/cDU are called.
if (typeof instance.componentDidMount === 'function') {
workInProgress.flags |= Update;
} // If shouldComponentUpdate returned false, we should still update the
// memoized state to indicate that this work can be reused.
workInProgress.memoizedProps = newProps;
workInProgress.memoizedState = newState;
} // Update the existing instance's state, props, and context pointers even
}
扩展:useState 更新
在react中触发状态更新的几种方式:
ReactDOM.render
this.forceUpdate
useState
useReducer
react 合成事件中改变状态是异步的,出于减少 render 次数,react 会收集所有状态变更,然后比对优化,最后做一次变更
effectList
至此render 阶段的绝大部分工作就完成了
还有一个问题:作为 DOM 操作的依据,commit 阶段需要找到所有有 effectTag 的 Fiber 节点并依次执行 effectTag 对应操作。难道需要在commit 阶段再遍历一次 Fiber 树寻找 effectTag !== null的Fiber 节点么?
这显然是很低效的。
为了解决这个问题,在 completeWork 的上层函数 completeUnitOfWork 中,每个执行完 completeWork 且存在 effectTag 的 Fiber 节点会被保存在一条被称为effectList的单向链表中。
effectList 中第一个 Fiber 节点保存在 fiber.firstEffect ,最后一个元素保存在 fiber.lastEffect。
类似 appendAllChildren,在“归”阶段,所有有 effectTag 的 Fiber 节点都会被追加在 effectList 中,最终形成一条以rootFiber.firstEffect 为起点的单向链表。
nextEffect nextEffect
rootFiber.firstEffect -----------> fiber -----------> fiber
这样,在commit 阶段只需要遍历 effectList 就能执行所有 effect 了。
你可以在这里看到这段代码逻辑。
借用 React 团队成员Dan Abramov的话:effectList 相较于 Fiber 树,就像圣诞树上挂的那一串彩灯。
例子:从渲染到performConcurrentWorkOnRoot在render结束会开启commit阶段
程序开头-->ReactDOM.createRoot
const root = ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root'))
console.log("=app=root:", root)
root.render(<Test />);
function createRoot(container, options) {
// 省略
console.log('%c=一切开始1:createRoot(', 'color:red', { createRoot: container, options })
var root = createContainer(container, ConcurrentRoot, null, isStrictMode, concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride, identifierPrefix, onRecoverableError);
markContainerAsRoot(root.current, container);
var rootContainerElement = container.nodeType === COMMENT_NODE ? container.parentNode : container;
listenToAllSupportedEvents(rootContainerElement);
return new ReactDOMRoot(root);
}
function createContainer(containerInfo, tag, hydrationCallbacks, isStrictMode, concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride, identifierPrefix, onRecoverableError, transitionCallbacks) {
var hydrate = false;
var initialChildren = null;
console.log('初始/更新-->FiberRoot:a-->createContainer')
return createFiberRoot(containerInfo, tag, hydrate, initialChildren, hydrationCallbacks, isStrictMode, concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride, identifierPrefix, onRecoverableError);
}
createFiberRoot-->FiberRootNode是初始化相关只调用一次
function createFiberRoot(containerInfo, tag, hydrate, initialChildren, hydrationCallbacks, isStrictMode, concurrentUpdatesByDefaultOverride, // TODO: We have several of these arguments that are conceptually part of the
// host config, but because they are passed in at runtime, we have to thread
// them through the root constructor. Perhaps we should put them all into a
// single type, like a DynamicHostConfig that is defined by the renderer.
identifierPrefix, onRecoverableError, transitionCallbacks) {
var root = new FiberRootNode(containerInfo, tag, hydrate, identifierPrefix, onRecoverableError);
return root;
}
function FiberRootNode(containerInfo, tag, hydrate, identifierPrefix, onRecoverableError) {
console.log('==FiberRootNode是初始化相关只调用一次===')
this.tag = tag;
this.containerInfo = containerInfo;
this.pendingChildren = null;
this.current = null;
this.pingCache = null;
this.finishedWork = null;
this.timeoutHandle = noTimeout;
this.context = null;
this.pendingContext = null;
this.callbackNode = null;
this.callbackPriority = NoLane;
this.eventTimes = createLaneMap(NoLanes);
this.expirationTimes = createLaneMap(NoTimestamp);
this.pendingLanes = NoLanes;
this.suspendedLanes = NoLanes;
this.pingedLanes = NoLanes;
this.expiredLanes = NoLanes;
this.mutableReadLanes = NoLanes;
this.finishedLanes = NoLanes;
this.entangledLanes = NoLanes;
this.entanglements = createLaneMap(NoLanes);
this.identifierPrefix = identifierPrefix;
this.onRecoverableError = onRecoverableError;
{
this.mutableSourceEagerHydrationData = null;
}
{
this.effectDuration = 0;
this.passiveEffectDuration = 0;
}
{
this.memoizedUpdaters = new Set();
var pendingUpdatersLaneMap = this.pendingUpdatersLaneMap = [];
for (var _i = 0; _i < TotalLanes; _i++) {
pendingUpdatersLaneMap.push(new Set());
}
}
{
switch (tag) {
case ConcurrentRoot:
this._debugRootType = hydrate ? 'hydrateRoot()' : 'createRoot()';
break;
case LegacyRoot:
this._debugRootType = hydrate ? 'hydrate()' : 'render()';
break;
}
}
}
可见children 就是root(根节点)
ReactDOMHydrationRoot.prototype.render = ReactDOMRoot.prototype.render = function (children) {
console.log('%c=一切开始3:', 'color:red', 'ReactDOMRoot.prototype.render调用updateContainer()开启render阶段==', { children });
var root = this._internalRoot;
// 省略函数
updateContainer(children, root, null, null);
};
开始2:render-->updateContainer()--scheduleUpdateOnFiber
function updateContainer(element, container, parentComponent, callback) {
{
onScheduleRoot(container, element);
}
var current$1 = container.current;
var eventTime = requestEventTime();
var lane = requestUpdateLane(current$1);
{
markRenderScheduled(lane);
}
var context = getContextForSubtree(parentComponent);
if (container.context === null) {
container.context = context;
} else {
container.pendingContext = context;
}
// 省略
var update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane); // Caution: React DevTools currently depends on this property
// being called "element".
update.payload = {
element: element
};
callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback;
// 省略
console.log('==render阶段准备:updateContainer调用enqueueUpdate()和scheduleUpdateOnFiber()==')
enqueueUpdate(current$1, update);
var root = scheduleUpdateOnFiber(current$1, lane, eventTime);
if (root !== null) {
entangleTransitions(root, current$1, lane);
}
return lane;
}
function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime) {
var root = markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot(fiber, lane);
console.log('==render阶段准备:scheduleUpdateOnFiber()调用ensureRootIsScheduled()==')
ensureRootIsScheduled(root, eventTime);
return root;
}
ensureRootIsScheduled-->performConcurrentWorkOnRoot
function ensureRootIsScheduled(root, currentTime) {
// 省略
if (newCallbackPriority === SyncLane) {
// Special case: Sync React callbacks are scheduled on a special
// internal queue
if (root.tag === LegacyRoot) {
if (ReactCurrentActQueue$1.isBatchingLegacy !== null) {
ReactCurrentActQueue$1.didScheduleLegacyUpdate = true;
}
console.log('%c=render阶段准备:ensureRootIsScheduled调用performSyncWorkOnRoot:异步更新legacy模式1==', 'color:red')
scheduleLegacySyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
} else {
console.log('%c=render阶段准备:ensureRootIsScheduled调用performSyncWorkOnRoot:异步更新legacy模式2==', 'color:red')
scheduleSyncCallback(performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
}
// 省略
} else {
// 省略
// console.log('更新流程-->0-c2: performConcurrentWorkOnRoot')
console.log('%c=render阶段准备:', 'color:red', 'ensureRootIsScheduled()调用performConcurrentWorkOnRoot--同步更新:concurrent模式==')
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback$1(schedulerPriorityLevel, performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root));
}
root.callbackPriority = newCallbackPriority;
root.callbackNode = newCallbackNode;
}
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot 这个函数在render结束会开启commit阶段
function performConcurrentWorkOnRoot(root, didTimeout) {
// 省略
console.log('%c==render阶段准备:重点函数performConcurrentWorkOnRoot,这个函数在render结束会开启commit阶段', 'color:red', 'color:cyan');
console.log('==render阶段准备:performConcurrentWorkOnRoot调用renderRootSync():同步更新concurrent模式:', { shouldTimeSlice });
var exitStatus = shouldTimeSlice ? renderRootConcurrent(root, lanes) : renderRootSync(root, lanes);
if (exitStatus !== RootInProgress) {
// 省略
if (exitStatus === RootDidNotComplete) {
markRootSuspended$1(root, lanes);
} else {
// 省略
root.finishedWork = finishedWork;
root.finishedLanes = lanes;
console.log(`%c=commit阶段=前=render阶段结束=performConcurrentWorkOnRoot调用finishConcurrentRender-->commitRoot`, 'color:cyan')
finishConcurrentRender(root, exitStatus, lanes);
}
}
// 省略
return null;
}
function renderRootSync(root, lanes) {
var prevExecutionContext = executionContext;
executionContext |= RenderContext;
var prevDispatcher = pushDispatcher(); // If the root or lanes have changed, throw out the existing stack
// 省略
do {
try {
console.log('%c=render阶段准备:', 'color:red', 'renderRootSync()调用workLoopSync()-root:', { root });
workLoopSync();
break;
} catch (thrownValue) {
handleError(root, thrownValue);
}
} while (true);
// 省略
workInProgressRoot = null;
workInProgressRootRenderLanes = NoLanes;
return workInProgressRootExitStatus;
}
图例
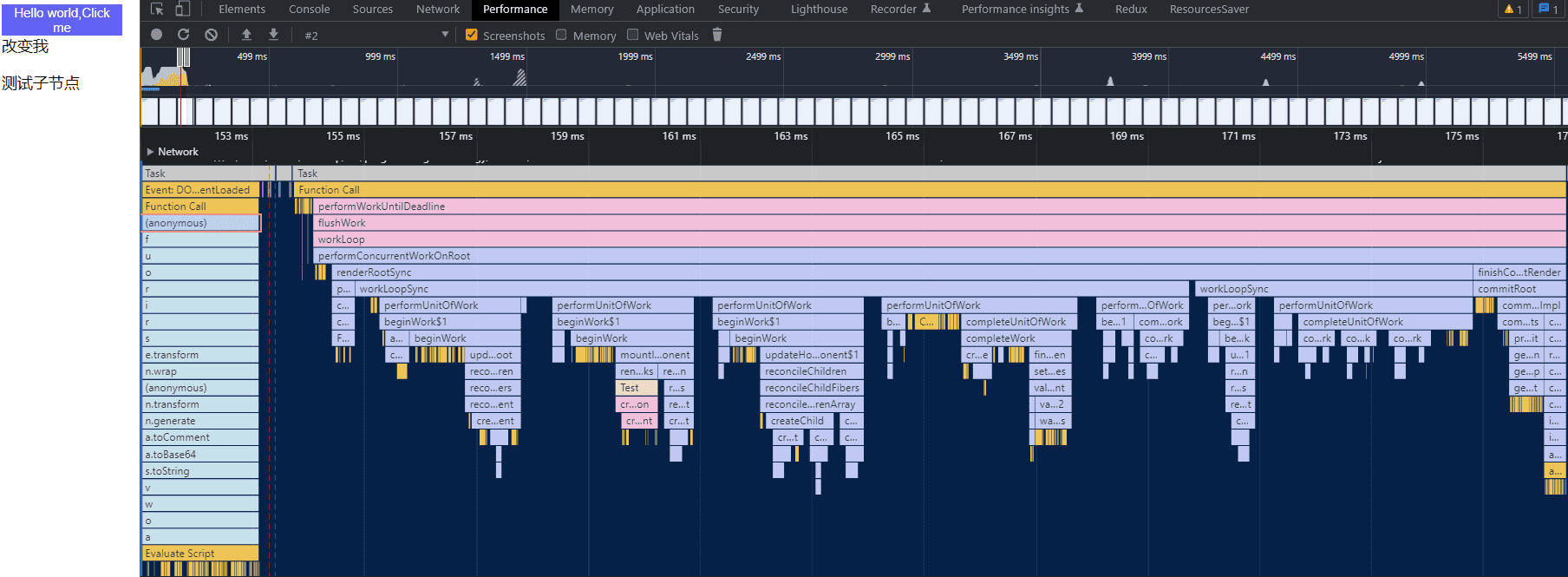
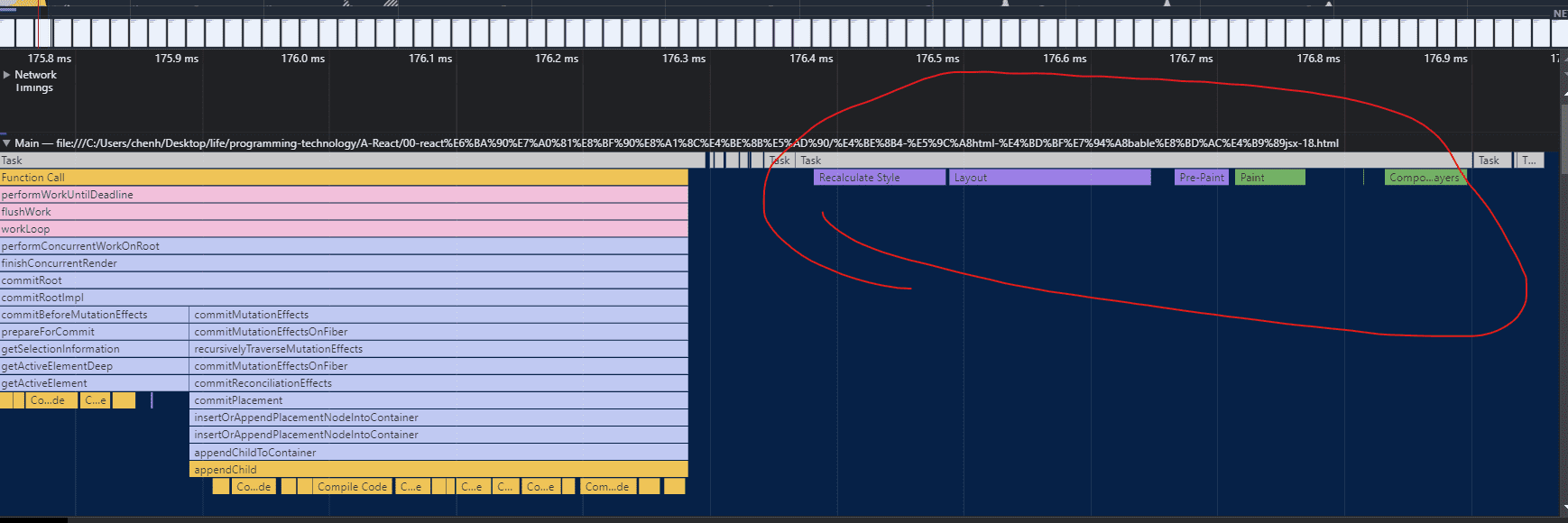
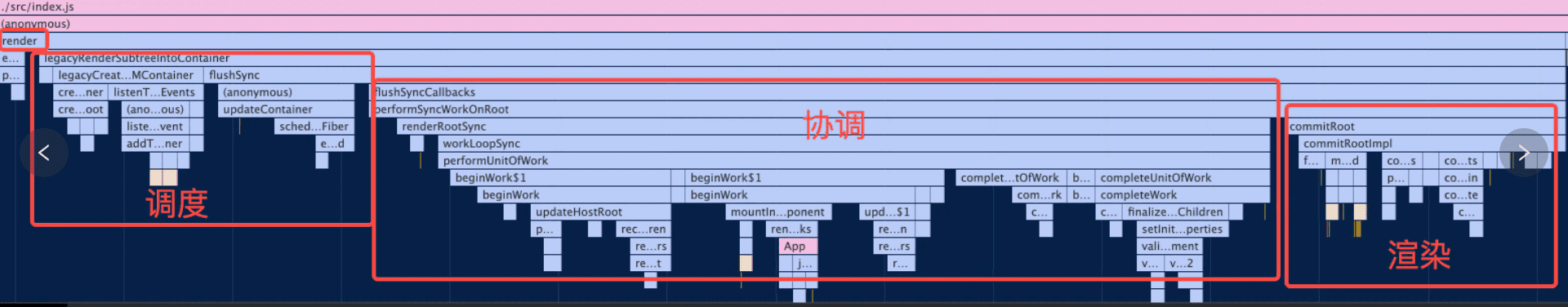
流程结尾:render 阶段全部工作完成
至此,render 阶段全部工作完成。在 performSyncWorkOnRoot 函数中 fiberRootNode 被传递给 commitRoot 方法,开启commit 阶段工作流程。
commitRoot(root);
这里以一个简单的jsx结构为例:
beginWork与completeWork这二者是如何相互配合共同完成fiber树的构建的。
return (
<>
<div>
<span>age: 18</span>
<p>
<span>name: zs</span>
</p>
</div>
</>
);
- 执行div的beginWork,创建第一个span1对应的fiber节点与p对应的fiber节点,同时会将span.sibling指向p,使得span执行完completeWork可以进入p的beginWork阶段
- 执行span的beginWork
- 执行span的completeWork
- 执行p的beginWork
- 执行span2的completeWork
- 执行span2的completeWork
- 执行p的completeWork
- 执行div的completeWork
最终会得到这样的一颗Fiber树:
至此,render阶段全部工作已经完成,我们得到了WIP以及对应的dom树,会被赋值给fiberRoot.finishWork,接下来的工作就是将渲染WIP,也就是提交阶段(commit)的流程。